As modern society is getting more multicultural, the IT market needs to adapt to these changes. That’s why, nowadays, having several localizations in mobile apps is no longer an optional feature but a necessity. This article will discuss the definition of mobile app localization, its purposes, and why it is helpful for businesses. It will also cover several technical aspects and tips for performing the localization of mobile applications.
What Is Mobile App Localization?
The process of software localization is no longer limited to merely text translation, as it was common decades ago. Instead, modern-day localization is a complex set of measures aimed at adapting a software product to different markets and cultures. Usually, the localization plan is detailed long before the product release, and the software development process takes this plan into account.
The core of the localization process is still the translation of text throughout an application. This includes the app’s interface, text on images and videos, and on any external resources, for example, PDF files or web pages that have links leading to them from within the app. This is the case, for example, when various documents, such as a user agreement or license, are presented as external files. This way, it is easier to amend them when necessary without extracting the required text from the application.
Cultural peculiarities are very important for localization. For example, this involves the support of different types of script, such as Latin, Arabic, Cyrillic, Chinese, and Japanese characters, and so on. Even the same language may still have large and small differences in various countries. They include spelling, the meaning of words, and other linguistic features created throughout the history of a particular language variant. Developers must also take these differences into account. That’s why, for example, Google Play supports seven variants of the English language, three variants of Chinese and Spanish, etc.
Another important element of localization is the choice of measurement units. Nowadays, the Metric system is generally adopted worldwide. However, three countries, including the USA, still officially use the Imperial system. Several states, such as Canada and India, occasionally use the Imperial system in certain contexts. For example, even though such countries adopted the metric system, inches are used there to measure the diameter of pizza, wheel rims, pipes and tubings, etc. This cultural feature may be important if a software product is targeted at those markets, especially in the case of online shopping or other retail apps.
If an app has audio speech resources, they may be localized as well. For most purposes, modern text-to-speech engines provide sufficient quality at a relatively low cost. Real voice recording is expensive, especially when it is performed by professional actors in specialized studios. Usually, only large development companies that release AAA-class mobile games, such as Activision Blizzard or miHoYo, have budgets for several voice-over language options. Their strategy is to offer users the best possible experience in their preferred language and maximize customers’ satisfaction that can lead to higher profits.
Localization also involves adapting software to those methods of payment and delivery services that are popular in the target region. For example, Mastercard, Visa, or Paypal may not be available in some countries, so an application must substitute them with local equivalents. The format of postal addresses also differs in many countries, which is important for retail applications.
And last but not least, in the case of mobile software, localization must include adapting software to the relevant requirements of Google Play and Apple Store. This process includes a translation of in-store titles, descriptions, and text on screenshots, adding keywords, and so on. If done properly, this will increase the ranking of the localized application, which will lead to more downloads.
Why It's Important to Localize Your App for Different Markets
Localization is essential to make a software product available in its target markets. If a mobile application supports many languages, it can cover larger audiences, earning more money. Moreover, it offers a better user experience and makes it much more comfortable to use the application. And a handy application is likely to become preferred among users and gain a competitive advantage over rivals.
Additionally, a well-performed localization shows users that the owner of an app decided to adapt it specifically for them. This means the owner increased the app’s budget to improve the experience of potential users as a sign of respect, to acknowledge the importance of that audience. This way, potential customers feel that this particular software is targeted at them and its owner is interested in their appreciation and support.
Benefits of Mobile Application Localization for Businesses
Software localization is a reasonable investment that greatly improves the final product and offers valuable advantages. They can be presented as three main benefits:

- Ability to reach a wider audience.
- More market coverage.
- Better user experience.
Together, these perks lead to more downloads and higher user count. Better user involvement leads to more profits from sales, advertising, or other monetization strategies utilized by an app. If it is an enterprise-oriented application, localization may improve productivity and interactions between offices and branches of a multinational corporation.
Technical Aspects
Localization (often shortened to “L10n”) is more effective if it is planned in advance together with internationalization (i18n). Here, internationalization refers to designing a future application in such a way that allows easy adaptation to different languages. That is, i18n is the development approach that promotes the L10n of an application without engineering difficulties.
Software developers have to foresee the necessity of editing the localized resources after the release. So, they have to find a way to extract only the required part of those resources, such as one string of text or one image. Additionally, specialists need to implement the possibility of integrating new localized resources into the existing application in a fast and seamless manner.
Extracting the text is just a part of the process. To make localization easier and more effective, it is necessary to maintain the original structure in the extracted text. This way, the localizing specialists will be aware of the context throughout the translation process. This is especially true when the interface has a lot of options, dialogue windows, or separate text elements, such as labeled buttons.
If software has a lot of text, especially in the case of mobile games or educational apps, developers need to ensure the consistency of terminology. This means the same specialized term or a proper noun must have the same translation throughout the whole text. Otherwise, users will be confused, for example, if they notice that the same interface menu is referred to as “Options,” “Settings,” and “Preferences.” One of the most effective ways of working with terminology is the use of translation memories and termbases that are stored in the cloud.
Tips and Best Practices of Localization for Mobile Applications
Here are a few tips to consider before planning localization for your mobile application.
- Research and select your target markets carefully. Extending the market coverage of a mobile application is tempting, but it is also costly and time-consuming. As a potential owner of a future mobile application, you need to devise its strategy. So, first of all, you have to decide whether you want to focus on one local market, several markets, or go global.
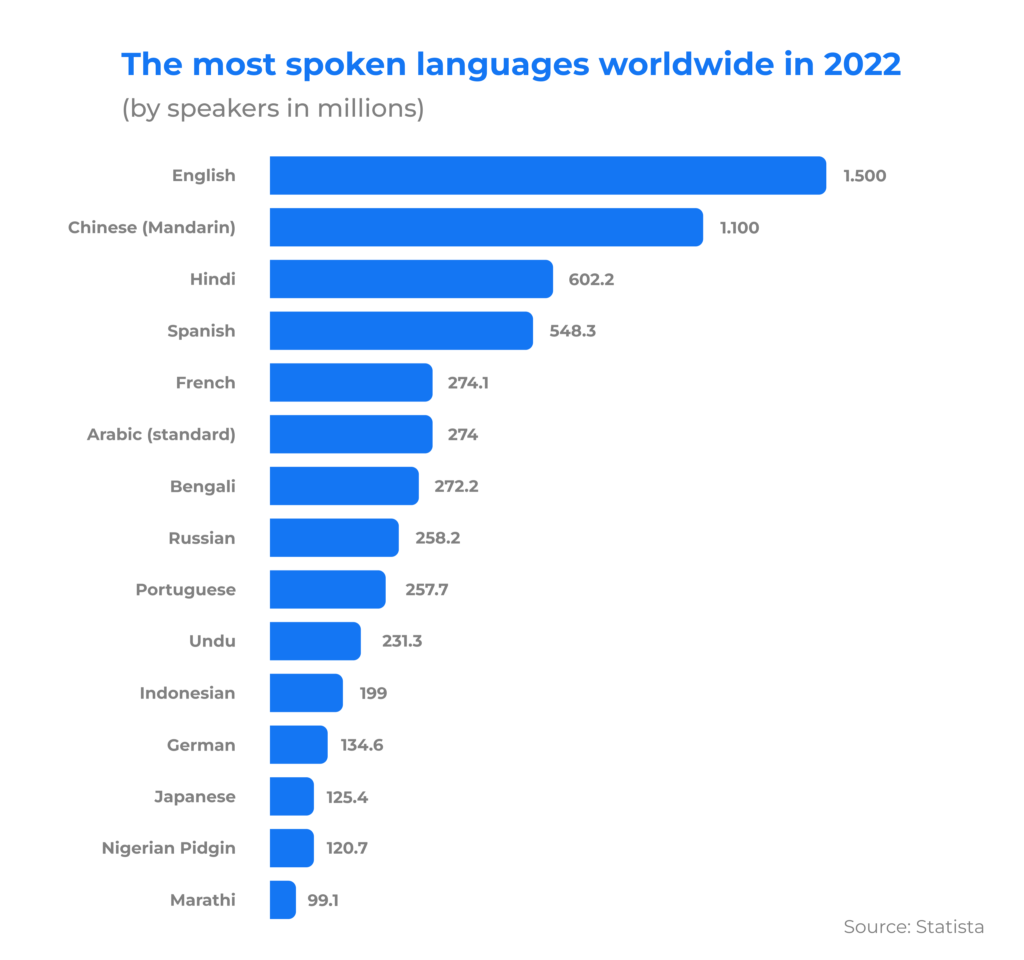
- Choose languages for your software. Usually, those are the languages of your initial and potential target markets. If you intend to launch your mobile app globally, you should consider covering at least five or six most spoken languages: English, Chinese, Hindi, Spanish, French, and Arabic.

- Prepare your software for localization. The ability to add localized resources must be provided by the design of an application. If this feature is implemented properly and in advance, it allows extending the market coverage of your mobile software even after its release.
- Choose a mobile app localization service provider depending on the budget. The process of software localization has changed a lot over the past years. Nowadays, it involves far less manual labor and more automation of routine and time-consuming tasks. This includes analyzing the software design and determining the resources that must be localized. Then, specialists need to extract those resources carefully to preserve their structure. The localization may be performed by the development company that builds your software if it has a relevant team. Otherwise, it may be done by a separate company that specializes in localization services. Crowdin, Onesky, Trados, and POEditor are among the most popular translation providers these days.
- Ensure the quality of localization. Quality assurance also applies to localization and should not be neglected. Translations should be approved by skilled editors and native speakers. The user experience of localized versions should be on the same level as in the original application.
Conclusion
Adapting software to different markets involves a lot of steps, so this brief article described just the tip of the iceberg. The process of localization is rather complex, even with the help of modern automated tools. It requires dedication and knowledge. It involves the hard work of translators, copywriters, editors, and other localization specialists.
To fully enjoy the benefits of mobile application localization, you need a competent team. Intellectsoft specializes in mobile development services and has experience in delivering software solutions for worldwide or local audiences. If you need a top-notch mobile application with the potential to go global or focus on a particular market, contact us.