With the development of computer technologies, cash payments are gradually becoming a thing of the past. Thanks to their convenience and safety, digital transactions have become a standard way of payment, even in offline shops and other business establishments. They improve customer satisfaction, add security and transparency to payment processes, and reduce risks associated with handling cash, including robberies and counterfeit money.
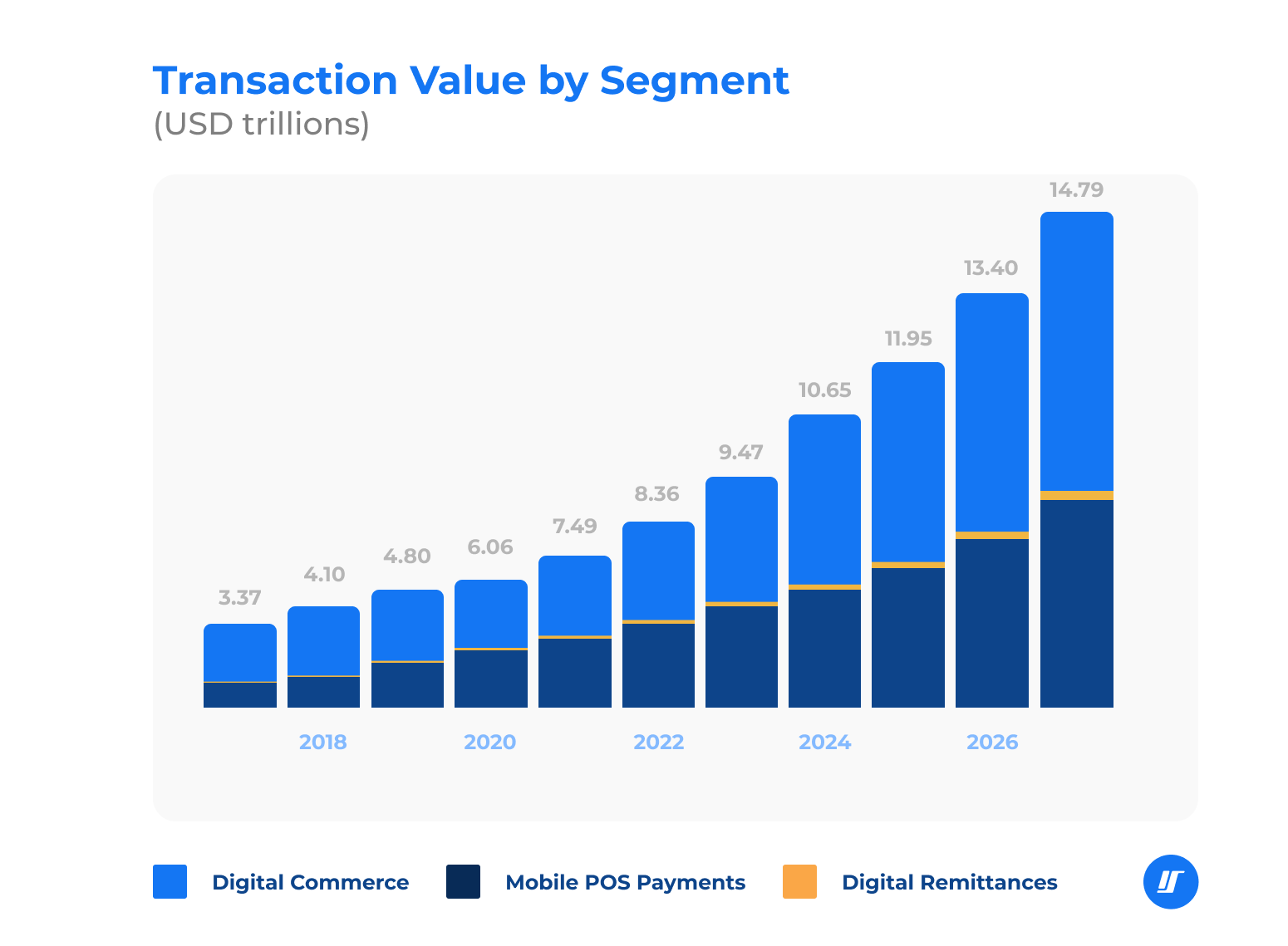
Since more businesses employ digital technologies, the popularity of online transactions is bound to grow. According to Statista, the global transaction value of digital payments is expected to reach 14.79 trillion USD in 2027. As a result, the need for payment processing services is also growing on a global scale.
In this article, we will define payment processing, examine its components, and review the benefits and drawbacks of its integration into custom software solutions.
What is Payment Processing?
In the context of cashless or online payments, payment processing is the sequence of steps that enable digital transactions between merchants and customers. The purpose of this procedure is to ensure the secure transfer of funds, such as mobile payments or transactions involving credit or debit cards, digital wallets, cryptocurrencies, and so on. Developing and maintaining a payment processing system is a very complex and resource-consuming process subject to strict regulations. On the other hand, integration of existing digital payment means into custom software is essential for businesses of all types and sizes. It is especially important for the retail e-commerce market, which is growing rapidly and is expected to reach 8.1 trillion dollars in 2026.
All digital payments may be roughly divided into three main areas: digital commerce, mobile POS (point-of-sale) payments, and digital remittances.
Digital commerce covers transactions made via websites or mobile apps using credit cards or online payment systems, such as PayPal. The most common example of digital commerce activity is online shopping, where customers browse goods and services and pay directly in an app or on a website.
Mobile point-of-sale (POS) payments generally involve using smartphones with mobile wallet applications or other devices with NFC chips, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, etc. Nowadays, many restaurants, stores, and other outlets use terminals that allow such contactless payments.
Digital remittance is a new way of money transfer between countries that offers several advantages over conventional methods. Instead of going to banks or other financial institutions, customers may use mobile apps or websites that enable a secure and convenient alternative with lower exchange rates and transaction fees.
Key Components in Payment Processing
Effective payment processing requires a well-organized cooperation of several components. Here is a brief description of these components, as well as some relevant terms.
- The Merchant. The merchant is the party that accepts the customer’s payment for provided or ordered goods or services.
- The Customer. The customer is the party that pays or promises to pay for goods or services provided by the respective merchant.
- Payment Method. The payment method encompasses credit or debit cards, digital wallets, and other means to conduct a payment operation.
- Payment Gateway. The payment gateway represents a specialized service that receives, encrypts, and securely sends payment-related data to the acquirer or the payment processing company from the connected POS system.
- Payment Processor. The payment processor is an intermediary company that performs and controls all technical aspects of transactions. These aspects include obligatory security procedures such as authorization, data validation, and so on. Currently, PayPal and Stripe are the most popular online payment processing systems, making them the most common choices for integration into custom software solutions.
- Point-of-Sale (POS) System. The point-of-sale system is a combination of software and hardware designed to receive customers’ payments at various points of sale, such as retail outlets, restaurants, etc. POS systems usually perform other tasks in addition to accepting payments, including tracking and management of inventory, staff, sales, and more.
- Acquiring Bank. The acquiring bank or merchant acquirer is a financial institution that holds the account of a business and receives payments from its customers’ accounts. To obtain the funds from a business transaction, an acquirer cooperates with the payment processor of a merchant and the issuing bank of a customer.
- Card Network. The card network is the provider of payment services that processes transactions made with credit cards and enables communication between the respective banks of the transaction parties. Some card networks, like Visa and Mastercard, allow their partner financial institutions to issue credit or debit cards connected to those networks. Meanwhile, other card networks, like American Express and Discover, issue their respective cards exclusively and act as both the issuer and the acquirer.
- Issuing Bank. The issuing bank holds the account of a customer and issues a credit card or a debit card as a payment instrument. The issuer authorizes or declines a transaction based on the request from the acquiring bank and the account information. According to IBISWorld, in 2022, there were 85 businesses that issued credit cards in the USA.
- Payment Security. Payment security encompasses various regulations, programs, and relevant technologies to protect payment information and verify its authenticity. This aspect is mostly governed by the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). The creation of this standard was a joint effort of several major card networks that required a more effective alternative to separate security programs in order to ensure data safety and prevent fraud. PCI DSS is regularly revised and updated to match the current challenges in the industry and design safer ways to process payments. The most recent version is PCI DSS 4.0, published in March 2022, which contains 12 main requirements described in detail on 360 pages.
How Does Payment Processing Work?
In a typical scenario, when a customer uses a digital payment to make a purchase from a merchant, the transaction process may be roughly divided into five basic steps. Here is a simplified description of the payment processing flow.
1. Interaction with the POS System
The customer interacts with the point-of-sale system at the merchant’s outlet by swiping a credit card or using contactless means. This interaction may also be performed by inputting the customer’s credit card number and a CVV code at the checkout page on an online store, for example. Then, the POS system sends data containing the required sum and the card information to the acquiring bank via the payment gateway.
2. Making Contact with the Issuing Bank
The acquiring bank receives the data from the previous step and contacts the customer’s issuing bank. Using the relevant card network, the acquirer informs the issuer about the transaction.
3. Verifying the Transaction Details
The issuing bank checks the validity of the sent information, including the credit card number, the CVV code, and the card expiration date. It also checks whether the customer’s account has enough money or credit to perform the payment. If this verification is successful, the issuing bank sends the authorization code to the acquiring bank using the same card network.
4. Performing a Sale
The approval of a transaction means that the issuing bank has reserved the required sum on the customer’s account and is preparing to transfer these funds to the merchant’s account in the acquiring bank. At this point, it is assumed that the customer has paid for the ordered goods or services even though the money has not been transferred yet to the merchant.
5. Forming a Batch and Settling the Transaction
Approved transactions are handled in batches. The merchant sends the daily batch of transactions with their authorization codes to the acquiring bank or the payment processor. The acquirer requests the sums defined in the batch from the issuer, which are then transferred from the customers’ account to the merchants’ account. Also, the applicable payment processing fees are collected in this process.
Importance of Payment Processing for Businesses
Even though payment processing is one simple action for a customer, business owners have to deal with its technical and much more complicated side. However, every business owner who has already implemented a payment processing system can indicate at least several tangible benefits they witness during every money transfer. Here are only a few advantages of payment processing for businesses and their customers.
Better Service and Customer Experience
A payment processing system is a tool that significantly reduces the wait time for financial transactions from days to seconds. At the same time, the system is responsible for the quality and the completion of every electronic transaction.
Thus, when a customer buys something, they only need to make a few taps or clicks on their devices. Possibly the most convenient payment system processing feature is the additional simplicity of refund or chargeback processes.
Enhanced Security
Dealing with sensitive information like the customer’s credit card and other personal data can be stressful for business owners in all industries. Trusted third-party payment processing systems or custom ones are safe to use because they are created with all required compliances (such as PCI certificates) that ensure customer data safety from all kinds of unauthorized access.
Reliable payment processing systems use encrypted channels to eliminate the occurrence of fraudulent transactions. Features like MFA (multi-factor authentication) and others make digital payments safe for customers and businesses they purchase from.
Cost Reduction
Dealing with paper checks and cash requires more actions when it comes to sending and receiving payments. As for companies, they commonly face banking fees, secure disposal charges, and additional costs when dealing with paper checks that, let’s face it, belong in the past as a payment option.
With a properly integrated payment processing system, business owners don’t need to hire accounting staff and minimize the department to 1-2 specialists.
Better Analytics and Reporting
Third-party payment processing platforms offer businesses advanced analytics and reporting functionality. With the help of this tool, you can track all payment transactions, monitor trends and performance, as well as detect problems and anomalies. Bespoke payment processing software can have absolutely any feature a company may need to streamline its business processes related to payments.
It is highly important for every business to have payment processing integrated into their platform by skilled and experienced professionals who know what they are doing. A poorly built and/or integrated payment processing system may result in losing time, money, customers, and reputation.
Challenges and Solutions in Payment Processing Development
The most difficult challenge for developers who build and integrate payment processing systems is compliance with regulations and ensuring the highest level of security. Another challenge is the constant modernization of fraud detection mechanisms in order to keep up with new threats. And finally, software developers should provide several payment methods for modern businesses. When a business accepts several ways to pay for goods and services, it brings more opportunities and improves customer experience.
The payment processing industry has prepared a unified standard, PCI-DSS, that contains guidelines and recommendations on how to solve security-related challenges. Compliance with this standard is the primary task for software developers who have to integrate payment processing services into their custom solutions. While banks, credit card networks, and payment processors have their means to deal with the mentioned challenges, software developers should provide additional security measures in custom solutions for businesses.
Conclusion
Payment processing systems can be a bliss to businesses when implemented and integrated properly and a curse when not. Depending on the size of your business, you have two options – use a ready-made payment-processing system like Stripe or build a custom one from scratch with the help of a reliable and certified software development vendor.
Whether you need to create a bespoke one for your company or want to properly integrate one into your business software, Intellectsoft is the team for you. For over 15 years, we have provided solutions for businesses of all sizes – from early-stage startups to SMBs and Fortune 500 enterprises. We have already successfully delivered more than 600 business solutions to clients engaged in healthcare, fintech, eCommerce, logistics, hospitality, automotive, and many other industries.
To learn more about our expertise in payment processing and other solutions, please see our most prominent Case Studies.
If you’re looking for a team to handle your problem with payment processing integration or need specific software to boost productivity and optimize your processes, don’t hesitate to contact us and tell us your requirements so that we can offer you the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
FAQ
What are the most popular payment processing technologies for businesses?
Mobile wallets combined with NFC hardware are popular thanks to the essential roles of smartphones in our everyday lives. Android and iOS have built-in mobile payment services, namely, Google Pay and Apple Pay, with their respective digital wallet applications. Several leading global producers of smartphones have developed similar payment solutions, such as Samsung Pay or Mi Pay.
As another example, blockchain, AI, and ML have also found applications in payment processing systems and provide numerous benefits and business opportunities.
What are the most demanded payment processors for online businesses?
PayPal and Stripe are the go-to choices for online payments in the world, and they provide many resources, such as APIs and SDKs, for software developers. Visa and Mastercard also offer developers their APIs to facilitate the integration of their services into software solutions. Finally, when developing a mobile application that requires payment processing, developers should consider the integration of the digital wallets mentioned in the previous section.